Table of Contents
Prevent SPAM issues
Why are SPAM filters rejecting an email?
Spam filters identify Spam based on a long list of criteria, but generally they consider:
- Relationship with subscriber
- Reputation of IP address and sender domain
- Quality of email subject line, teaser, and content
- Quality and safety of links in email
- Presence or absence of images (e.g. tiny size of a tracking images might cause a problem)
- Ratio of images to text and links to text
- Inclusion of text version of email
- etc.
How can I get pass the common email defenses like SPAM filters?
The goal of a phishing campaign is people testing. So you don't want to spend too much time in creating a hack that allows you to bypass an external email filter (as most email filters are "black boxes" the only way of preventing you from being filtered is using some very time consuming trial & error methodology). Therefore we strongly recommend creating a whitelist entry on your SPAM/Email defense solution (whitelist either LUCY's domain or IP).
What can I do, when my emails get filtered?
Use an external mail server Using an external mail server with an existing domain configured could be the easiest and quickest workaround to prevent SPAM issues.
Set helo/ehlo SMTP host name in LUCY (only required if you use LUCY's build in mail server) It is recommended to create a SMTP server name (that is the server name of LUCY). Most SMTP servers will accept your mail if you simply have a reverse DNS entry. It does not have to match the domain name on your e-mail address. Some SMTP servers will reject mail if the reverse DNS doesn't match the HELO/EHLO hostname used in the connection. If your mail server's hostname is mail.example.com then your reverse DNS, MX record, HELO/EHLO, and SMTP greeting banner should all be mail.example.com as well. According to RFC 2821 the SMTP client MUST, if possible, ensure that the domain parameter to the EHLO command is a valid principal host name (not a CNAME or MX name) for its host. If this is not possible (e.g., when the client's address is dynamically assigned and the client does not have an obvious name), an address literal SHOULD be substituted for the domain name and supplemental information provided that will assist in identifying the client. An SMTP server MAY verify that the domain name parameter in the EHLO command actually corresponds to the IP address of the client. You can save this under the mail Settings:
Review Your Email Content Spam filters consider a long list of criteria when judging the “spamminess” of an email. They’ll weigh each factor and add them up to determine a Spam score which then determines whether a campaign will pass through the filter. They might look for spammy phrases like “CLICK HERE!” or “FREE! BUY NOW!”. Then they'll assign points every time they see one of those phrases. Certain criteria get more points than others. Here’s a sample of criteria from SpamAssassin:
- Talks about lots of money (.193 points)
- Describes some sort of breakthrough (.232 points)
- Contains urgent matter (.288 points)
- Money back guarantee (2.051 points)
LUCY allows you to review the mail content with the local SPAM assassin engine:
Don't use a private account as your sender address If you use a major ESP and send email using personal email addresses such as paul@yahoo.com or paul@aol.com, ISPs like Google will block your email. Why? Yahoo and AOL tell them to! The solution is to use your corporate email address or a domain owned by you. But please watch out: if your Company domain is "mycompany.com", you probably won't be able to use this domain as a sender as spoofing attempts are most likely detected if your domain has a SPF entry. You can validate this here: https://mxtoolbox.com/spf.aspx
Use Descriptive Text Instead of URLs as Link Text Spam filters try to block phishing attacks where attackers encourage readers to click on a well-known text URL that links to a different URL (attacker website). For example, a victim of a phishing attack would see "http://chase.com" in an email but upon clicking the link, they would be directed to "http://attackerwhostealsyouridentity.com". Because of this shady tactic, you should avoid using URLs as link text. Instead, use descriptive text.
Make Sure You Are Not on Blacklists If you are sending from your own IP address, you can use tools like MX Toolbox (https://mxtoolbox.com/blacklists.aspx) or LUCY's build in checks to verify and get alerted if your IP gets on a blacklist.
It Matters Where You’re “From” Mailbox providers evaluate more than just the sender’s IP, domain and content. They also pay attention to your "From" field addresses. Therefore avoid obscure From field names, such as: “1338sdsd8@domain.com”, “noreply@domain.com”. Use clear, trustworthy From field names, such as: “contact@”, “newsletter@”, “support@”, feedback@”
Keep the Format Simple Avoid the use of background colors, large or unusual fonts, or more than one font. In other words, don't make your email look like an advertisement or a brochure. Avoid coding sloppy HTML - usually from converting a Microsoft Word file to HTML. Avoid creating an HTML email that’s nothing but one big image with little or no text. Spam filters can’t read images, so they assume you’re a spammer trying to trick them. Using the word “test” in the subject line. Agencies can run into this issue when sending drafts to clients for approval.
Limit the Number of URL Links Spam filters are wary of link-laden messages because spammers tend to scatter links around their messages, hoping that the reader will click on at least one.
Create a Unique Subject Title In your e-mail header, include something unique to the recipient that's unlikely to be in a Spam message. Examples could include your company name, the name of one of your target's competitors, or the name of a person with whom the target is already familiar.
Review Your Sending Method and Ask Your Client to Whitelist the IP Sending a test to multiple recipients within the same company might cause some problems. That company’s email firewall often assumes it’s a Spam attack. To perform a phishing attack, you might need to whitelist LUCY's IP on the remote firewall or SPAM filter.
Optimize your DNS settings Don't use an existing common domain name (like apple.com) already reserved by a third party. Never use a domain that does not exist. Reserve a similar domain name or one that relates to the service you describe in the email (example: get-your-secure-mail.com). Set an MX, A & a SPF record for the domain you use in the test that all point to LUCY for that domain. Enable LUCY's DKIM feature and save the corresponding DNS txt record. Also check: Did you use an email address with a domain that points to a different MX record? If you use attacker@gmail.com as an example for the sender most email servers will block that email since LUCY is not the official email server for this service.
Does the sender domain even exist? If you use a non-existing domain address as a sender or a domain which has no MX record, the mail will most likely be dropped by your mail server
Watch out when you spoof your own domain or use a domain which is SPF protected Did you define your own company domain as a sender? Example: You try to phish your employees with the domain mycompany.com which is actually the official domain for your company? The problem is that there might be a DNS record (example SPF) that defines which mail server is allowed to send mails on behalf of this domain. You can check this here: https://mxtoolbox.com/spf.aspx. If such a record exists your email server will deny emails coming from a different server using this domain. The solution is: If you still want to perform a phishing test, with a domain like the one from your company, we recommend reserving a similar domain like “my-company.com” or strategically place a typo like “myconpany.com”. Most users won’t recognize the difference and you'll have an additional feature to test awareness.
Set a PTR (reverse DNS) Some SPAM filters like http://www.spamcannibal.org/ will put an IP address without a valid PTR & A-Record on a blacklist. To prevent this, we recommend defining a PTR (reverse DNS) for the IP address where LUCY is installed and sending mails. This must be a unique FQDN (like testing.example.com). You still will be able to associate more than one domain with LUCY. But it is only possible to define one PTR per IP. The PTR record can only created by your provider or us (in case you order our VPS).
Avoid using a tracking image in the mail (Do not click: "track opened mails") Tracking images (the small size) lead to a higher SPAM score. So try to uncheck this option in case you get filtered.
Avoid using advanced LUCY Features like "advanced information gathering" The advanced information gathering is often detected by scanners that follow the links. This will raise the chance your mail gets flagged as SPAM.
Test your IP & Domain reputation If you mails still get flagged you can test your domain/reputation (see details in this article: https://sendgrid.com/blog/5-ways-check-sending-reputation/).
Don't send too much at the same time If you send hundreds of mails without throttling down the delivery you might get flagged as SPAM very quickly. Please use the scheduler to slow down mail delivery.
Avoid potentially dangerous attachments Certain attachment types (e.g. exe within a zip) or word files with Macro's are automatically classified as dangerous and most likely will end up in SPAM. Rather provide such files as a download on the LUCY landing page than attaching it to an email.
What is the best test procedure with LUCY to identify the source of SPAM issues?
Step 1 - TEST MAIL Send to the desired recipient a test mail using a sender with a 3rd party domain name that has no SPF (e.g. "test@gaga.com; you can test the SPF here: https://mxtoolbox.com/spf.aspx) or a valid domain (valid means, that the domain has a MX record) configured on LUCY.
The test mail is always a text only mail with no suspicious content.
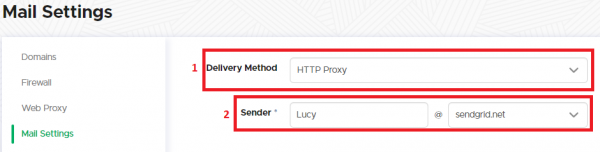
If the test mail does not arrive it is possible that the email filter is blocking any mail communication from an unknown IP or an server with a neutral mail reputation (if there is no known activity log about that IP in the internet). In such a case you can try to configure an external mail server. If you don't have a mail relay you can use, please set for the test the mail delivery method to (1) "HTTP Proxy" in the "settings/mail settings" menu and use one of the predefined domains (2):
This will force all communication through the external mail relay from sendgrid. You can change this setting later on a campaign level (under "Base Settings/Scenario Settings/Mail Settings").
Step 2 - IDENTIFY THE ISSUE THAT TRIGGERS THE EMAIL FILTER If the test email arrives, you can start altering the message & domain settings: it is very important that you change the settings step by step, in order to identify the reason for getting filtered.
One of the first changes you might want to try is playing around with different domain names (e.g. a different domain as a sender mail, the using a different domain for the landing page and maybe also just use a link with an IP address only). If there is no effect in using different domain names make sure that the domain settings are correct. Keep the mail & landing page as simple as possible in the beginning and then start adding content.
Step 3 - TEST RUN After you identified and removed the issues that caused the mails to get filtered we recommend doing a test run. The test run should be done with one target email accounts to see if the email gets filtered and how the link is accessed (sometimes a SPAM filter can automatically access the link in the email before the user can. This will make it impossible for LUCY to know if the link was really clicked).
Step4 - REAL CAMPAIGN Once you started the campaign you might still have a situation where mails get filtered. To investigate this:
- First check if the mail got send by clicking on the message log in the left navigation panel within a campaign
- Then check if there was a communication error by clicking on the error log in the left navigation panel within a campaign
There are three possible message scenarios in case mails are still being filtered:
- a) No mails send: then you won’t see anything in the message log
- b) Mails send – but with error: then you will see an error in "Errors"
- c) Mail send – no error: mail communication has been established and mails have been accepted for delivery
In case of "c" (if there is was no obvious error) you have two possibilities:
- 1) You know that the SMTP communication works and LUCY's IP is not filtered by any 3rd Party product. Therefore you experience a configuration issue in the campaign which causes the mail to get filtered (like using a spoofed sender domain which has an SPF record, using a sender domain that points to a different MX record or has no valid MX record at all or creating a campaign that gets filtered because of the SPAM score). Also make sure you even created a message template in the campaign). If the test mail does not go through: make sure port 25 is opened on your router/firewall and mails do not get filtered by SPAM filters. In case the firewall configuration is not allowing LUCY to send mails, you might also configure LUCY to use an external mail server. See using_an_external_mail_server_or_web_proxy.
- 2) Investigate your settings
- 3) In some cases there is a email threshold that limits the amount of emails you are allowed to send in a certain time frame. Amazon, Google & Microsoft have such limits. When you do a test run you might not experience any difficulties, but once you start sending out mass emails, the communication might get dropped by the remote mail server.
Known Issues with Microsoft, Gmail etc.
Some providers will block all mails or automatically flag them as SPAM from any new mail server that has no activity logs in the internet (like Microsoft or Gmail). Microsoft Points out that any new mail server will have a higher likelihood of getting blocked (https://mail.live.com/mail/troubleshooting.aspx). In any case you could also request to get whitelisted (here a link for Microsoft: https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/getsupport?oaspworkflow=start_1.0.0.0&wfname=capsub&productkey=edfsmsbl3)
Note: If you are sending emails from a new or “cold” IP address, abrupt spikes in email sending volumes can harm your IP’s reputation. To prevent this, you need to warm your IP address up gradually over time to establish your IP address as a legitimate email sender among Internet Service Providers (ISPs). Properly warming up your IP address is a crucial step in building your email sending reputation and improving delivery performance. The key to warming your IP address is to spread out your initial sends over multiple days. If you cannot do that, use a our HTTP mail delivery method. This method will send the emails through trusted mail servers using Sendgrid's mail infrastructure.
How do I improve my Sender Score?
Your Sender Score can affect your deliverability in a few ways. Senders with scores below 70 generally have emails coming from their IP aggressively filtered – your emails are more likely to end up in junk folders. Senders with scores above 70 generally have filtering applied to individual emails and campaigns, rather than their IP address.
There are several things you can do to improve and maintain a good Sender Score. Maintaining consistent sending volumes and schedules, staying off blacklists, and warming your IP address are all great ways to keep your Sender Score healthy.
My IP got blacklisted. What can I do?
You want to be removed from any blacklists because databases often share IP addresses that have been listed. If you you've fixed things on your end, go back to the blacklist's site and follow their instructions for the IP address removal process. Here's what you're likely to come across:
- Self-Service Removal. There are a few blacklists with a self-service removal feature that lets you take your IP address off the list without much trouble.
- Time-Based Removal. Most blacklists have a built-in, automatic process that removes lower-level listings (IP addresses that are light offenders) within a week or two. But if the IP address had sent spam more than once or did a high volume, the time period will be longer.
In case you rent a VPS through LUCY Security, we kindly ask you first to contact the the blacklist site and request a de-listing. If you cannot get delisted in a reasonable time, please get in contact with us and we can request an IP address change.
"Deceptive site ahead". What can I do?
If you are seeing a message like this, it means that the domain name was blacklisted by Google.
Here are the different methods to resolve the issue (in order of recommendation):
Option 1. Perform the Google Whitelisting procedure.
To whitelist the domain please review this article:
Google Safe Browsing
Option 2. In case Option 1 doesn’t work, it's advised to choose another template for the Phishing Scenario and try again using the same domain in the scenario settings.
Option 3. This option is the extended version of Option 2, but at this point also change the domain in the scenario settings. For the domain configuration please refer to a dedicated article Domain Configuration.
Option 4. Repeat the recommended steps from Options 2-3 and check the domain status for the existing issues in the search console:
https://search.google.com/search-console/
Then fix the issue and send the site again for a review confirming that the issues have been eliminated.
Please refer to Google Safe Browsing at this step.
Option 5. The fastest and easiest option is to abandon the current domain name and register a new one. The registration process is described here: Domain Configuration.
Option 6. In case if LUCY administration domain got blacklisted, there's a way to still be able to access it, but this would require the deactivation of Safe Mode, which is not recommended.
If access is needed urgently, follow these steps (WARNING! This setting is applied globally for the browser!):
- Open Chrome
- Go to Settings > Privacy.
- Toggle off Chrome's Safe Browsing mode.
After the actions above, the Deceptive Site message won't appear in your browser and the LUCY administration panel is available again.
You can check if your domain got blacklisted by Google via the link below: https://transparencyreport.google.com/safe-browsing/search
Whitelisting in different products
GSuite/Google Apps
Please review this article.
Office365
Please review this article.
Proofpoint
- From your Proofpoint admin center, navigate to Email Firewall, then Rules.
- Select the "On" radio button for Enable, under Rule Settings.
- Name your rule ID
- In the "Condition" section whitelist LUCY's IP addresses using the "Add Condition" button.
- Under Dispositions, change the Delivery Method from the default selection to Deliver Now.
- Save your rule and allow time for this new setting to propagate before testing.
Baracuda
- Log in to your Barracuda Email Security Gateway web interface.
- Go to the BLOCK/ACCEPT > IP Filters page.
- In the Allowed IP/Range section, enter the LUCY IP in the IP/Network Address field.
- In the Netmask field, type 255.255.255.255.
- Click "Add" to whitelist the IP address.
- You might need to whitelist us in Barracuda's Intent Analysis feature to prevent the URLs in simulated phishing tests from being altered. Here is an article from Barracuda about this topic: https://campus.barracuda.com/product/emailsecurityservice/doc/3211276/intent-analysis-inbound-mail/?welcome-to-campus=techlibrary
- If you'd like to spoof your own domain, you can exempt Trusted Forwarder IP addresses from SPF checks. Here is an article from Barracuda about this:https://campus.barracuda.com/product/emailsecuritygateway/doc/3866643/sender-authentication
Forefront Protection 2010 for Exchange Server
- In the Forefront Protection 2010 for Exchange Server Administrator Console, click Policy Management, and then under the Filters section, click Filter Lists.
- In the Filters – Filter Lists pane, click the Create button.
- In the Select Filter Type dialog box, select Allowed senders and then click Next.
- In the Filter Details dialog box, specify the filter list name and filter details
- In the Filter list name box, type a name for the new list.
- In the Filter criteria box, type the e-mail address or e-mail domain to be included in the filter list, and then click Add.
- User addresses should be entered in the following format: user@customer.com
- E-mail domain names should be entered in the following format: domain.com, domain.edu, domain.org, and so on. You can repeat this process in order to add multiple addresses or domains, or you can add multiple items on the same line, provided that they are separated by a comma.
- To configure the filtering options that will be bypassed for the e-mail addresses or domains specified in the list, you can select the following check boxes: File—Skips file filtering. Keyword—Skips keyword filtering. Content—Skips subject line and sender-domain filtering.
- Click Next.
- In the Target dialog box, configure how you want the filter list to be applied to the Hub/Edge Transport Scan. To enable the filter list for use with the transport scan, using the Enabled drop-down list, select Yes (this is the default).
- Click Create.
- The filter list you just created appears on the Filters – Filter Lists pane.
- Click Save.
MessageLabs or Symantec
To add a global Approved Sender:
- Select Services > Email Services > Anti-Spam.
- Ensure that Global Settings is selected in the domains drop-down list.
- Click the Approved Senders tab.
- Click the Add Entry option.
- The Domain/Email/IP and Description fields become editable.
- In the Domain/Email/IP field enter the IP address of the LUCY server.
- In the Description field, enter brief details about the new entry.
- To add the entry to the list, click Update.
This new policy will allow any inbound mail flow originating from LUCY's IPs to reach your users.
Catenator scripted module
Any LUCY instance can be optionally hardened with the additional scripted module Catenator. It allows intercepting and redirecting requests that analyze phishing activity, minimizing the chance of LUCY instance to be blocked / blacklisted. More info here